Technical Article
-
Technical Overview of MEMS Microphone Output Interfaces: From Analog Architectures to Multi-Channel Digital Transmission

The output signal of ECM (Electret Condenser Microphones) is almost all analog, most of which are single-ended. However, in contrast to MEMS Mic, there are two types of output interfaces: "Analog" and "Digital". Analog is also divided "Single-ended" and "Differential" outputs and digital output, which contains "PDM," "I2S," and "TDM" outputs. PDM occupies the most significant proportion.
The following introduces the MEMS Microphone output interface categories:
1. Analog Single-ended: This is a commonly used format, and the price is usually lower than the Differential type. The sensitivity is generally in the range of -38dBV ~ 40dBV. All the audio codec microphone inputs support this signal and make it the most popular one. But when designing the PCB circuit for this kind of microphone, noise can be avoided referring to Fig. 1
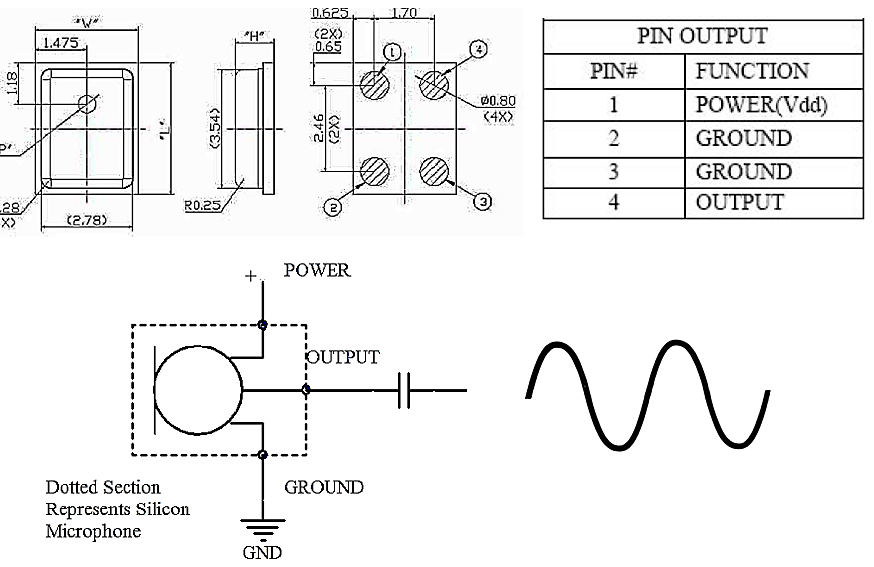
2. Analog differential-ended: This type is uncommon, and the price is usually higher than Single-ended. It is a Differential Output. Therefore, the sensitivity will also increase by 6dBV. The sensitivity is generally set around -32dBV, and it can also increase the AOP (Acoustic Overload Point). Most audio codec microphone inputs also support this signal. Fig. 2 helps noise reduction, and Common mode noise could be eliminated by using differential circuitry. Fig 2-1
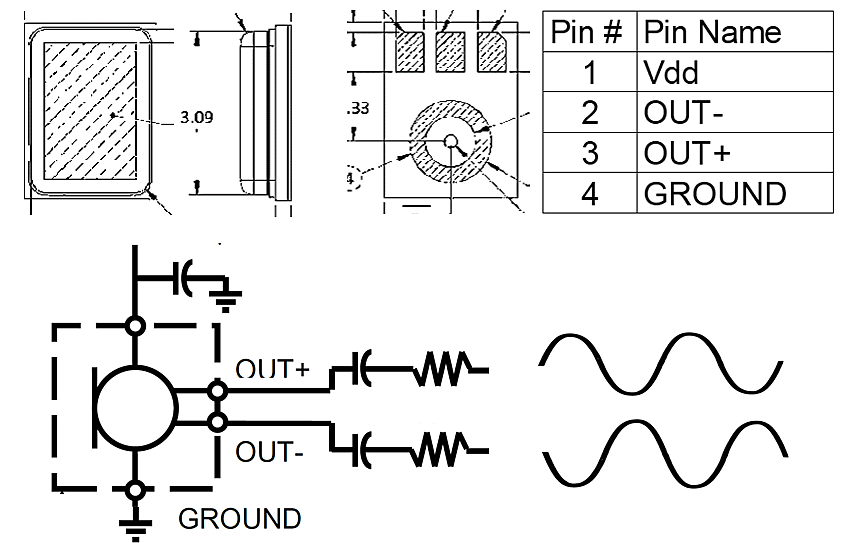
Fig.2 Analog MEMS Mic differential ended
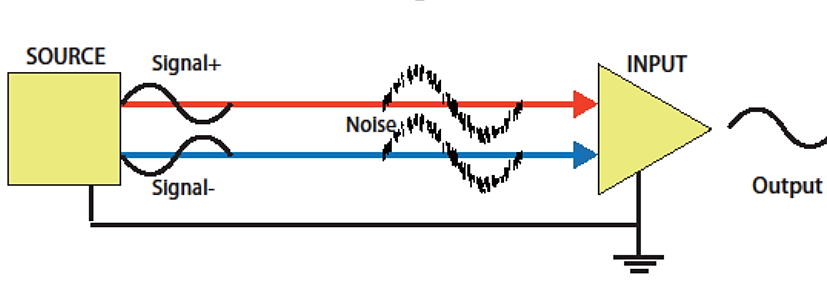
Fig.2-1 Differential Common Mode
3. PDM (Pulse Density Modulation): It is the main output interface of a digital MEMS microphone. The L/R channel shares the Data BUS, so it only needs four lines to complete the stereo L/R channel transmission; it is also suitable for the PCB layout design of portable devices. It is digital and requires a clock signal (usually 1MHz to 4MHz), so the audio bandwidth can meet the application of 20Hz to 20KHz, widely used in consumer electronics, automotive, and IoT devices. Fig.3
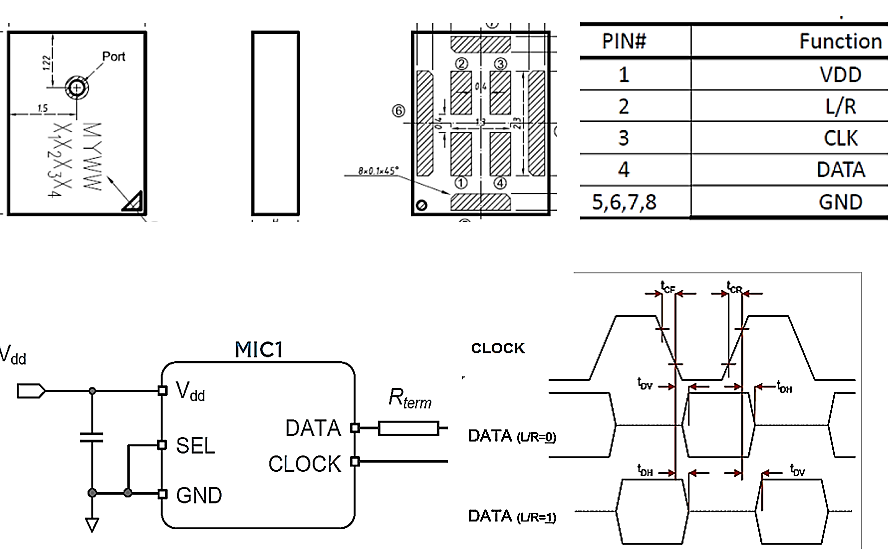
Fig.3 Digital MEMS Mic PDM Interface
4. I2S (Integrated Internship Sound): This digital audio serial bus standard format was developed by Philips to transmit audio data between digital audio devices. The bus is used explicitly for data transmission between audio devices, widely used in various multimedia systems. Most entry-level MCUs don't support PDM interfaces but basic I2S interfaces. Therefore, some microphone manufacturers have still launched I2S MEMES microphones for applications without an audio codec. Fig.4
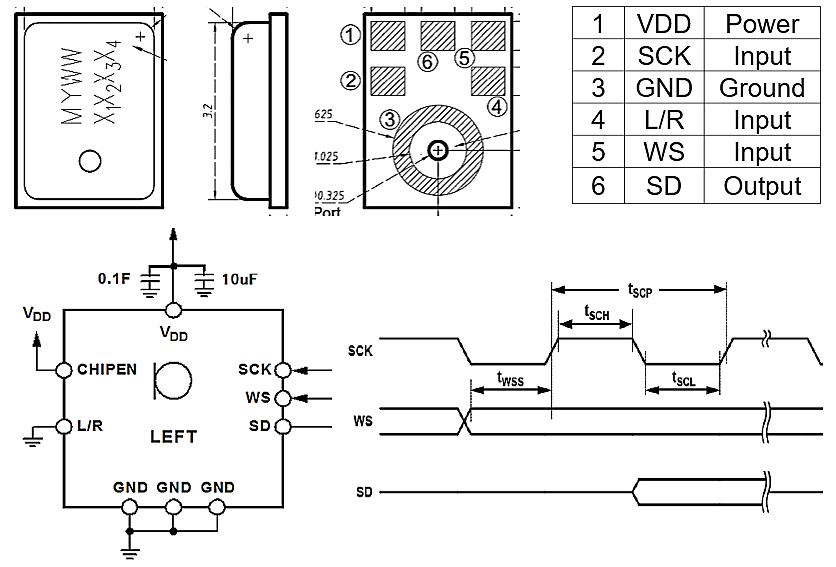
Fig.4 Digital MEMS Mic I2S Interface
5. TDM (Time-division multiplexing): It divides the usage time of the transmission medium several fixed time slots. Each time slot occupies a short period (for example, 20ms) and is considered a virtual channel. When data are communicated, the two interconnected parties will be set to transmit data in a particular time slot. It has the right to use the transmission intermediary for a specific time. For a longer time, the entire transmission intermediary is the same as having multiple connections, and they send data simultaneously. And because the smart speaker needs to perform "Far-Field Voice Pickup" when the Beamforming microphone can no longer meet the criterion, the 6 to 8 pcs microphone array has been developed. An increase of microphones means more channels are needed (ex., PDM and I2S); thus, to reduce the number and cost of microphone digital interfaces, TDM time and division multiplexing are used to transmit signals to achieve low-cost multi-channel transmission.
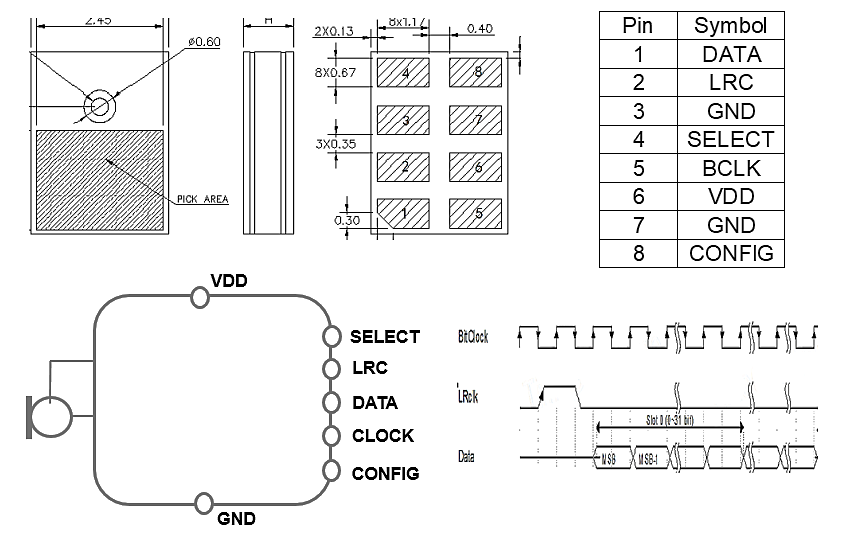
Fig.5 Digital MEMS Mic TDM Interface
6. Conclusion: The above introduces various microphone output formats. The correct microphone specifications can be selected according to product application requirements to meet the design criteria of high performance and low cost.

 RFQ
RFQ